Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation Promotes Survival and Supports Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Middle-Aged Mice: Cell Metabolism

IJMS | Free Full-Text | The Critical Role of the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Catabolism-Regulating Enzymes, Branched-Chain Aminotransferase (BCAT) and Branched-Chain α-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase (BCKD), in Human Pathophysiology
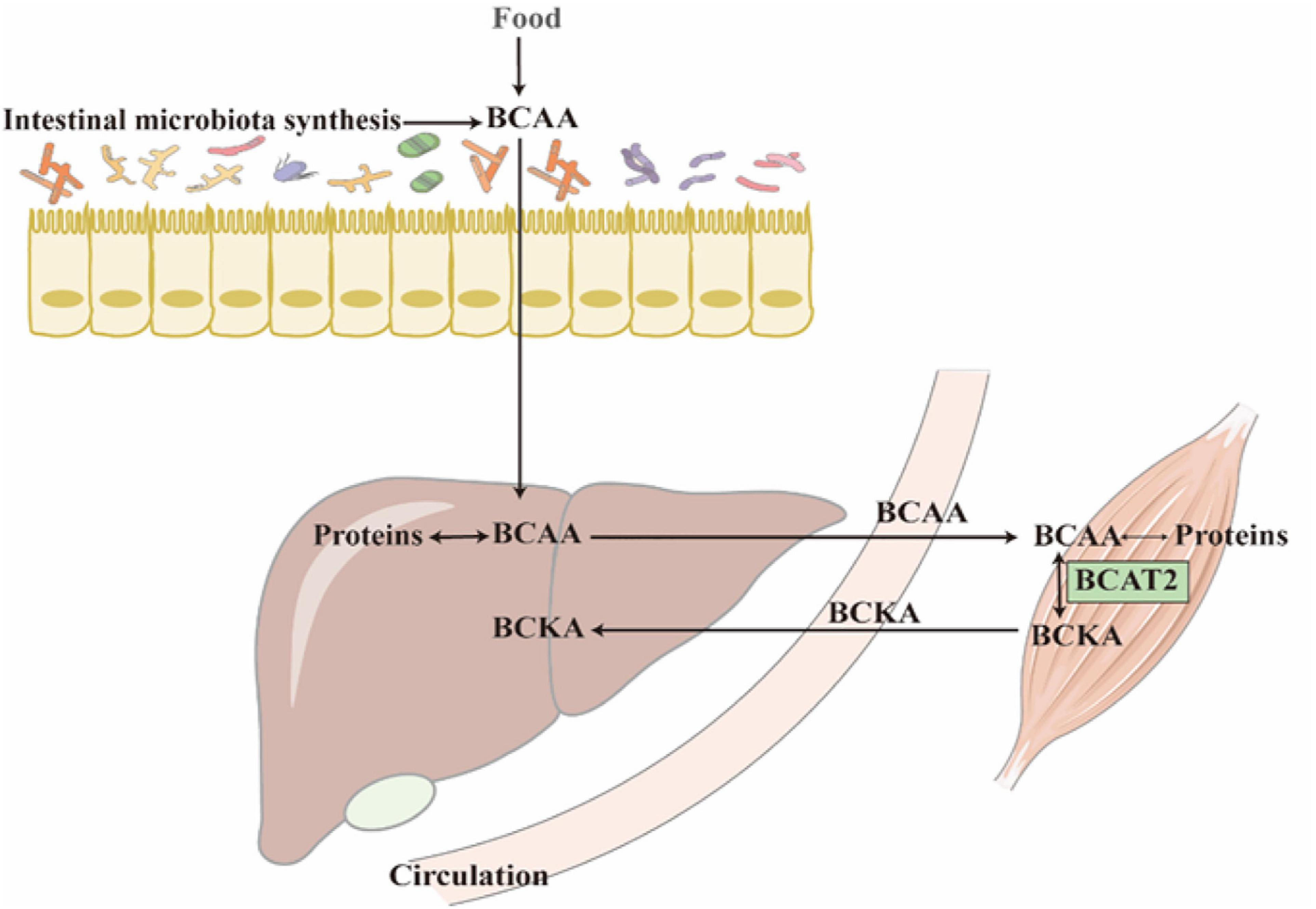
Frontiers | The Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Branched-Chain α-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase Kinase in Metabolic Disorders
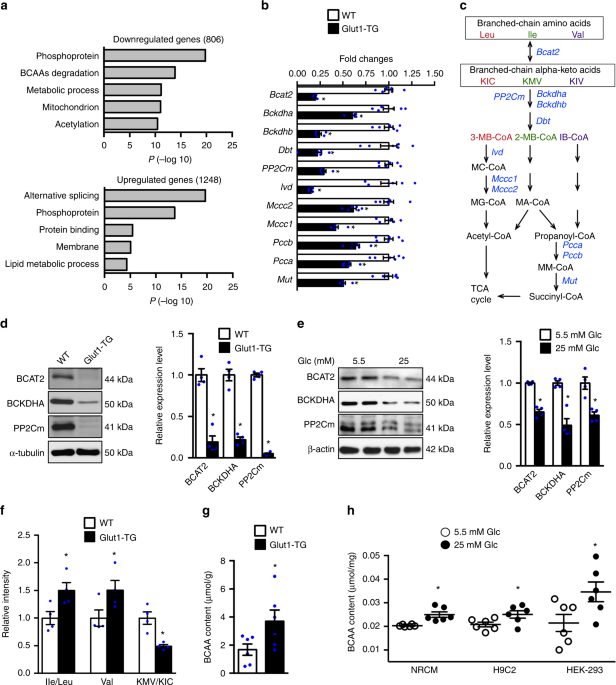
Glucose promotes cell growth by suppressing branched-chain amino acid degradation | Nature Communications

Metabolic flux analysis of branched-chain amino and keto acids (BCAA, BCKA) and β-hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid across multiple organs in the pig | American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism

Food consumption of branched chain amino acids and insulin resistance: A systematic review of observational studies in humans - Clinical Nutrition ESPEN
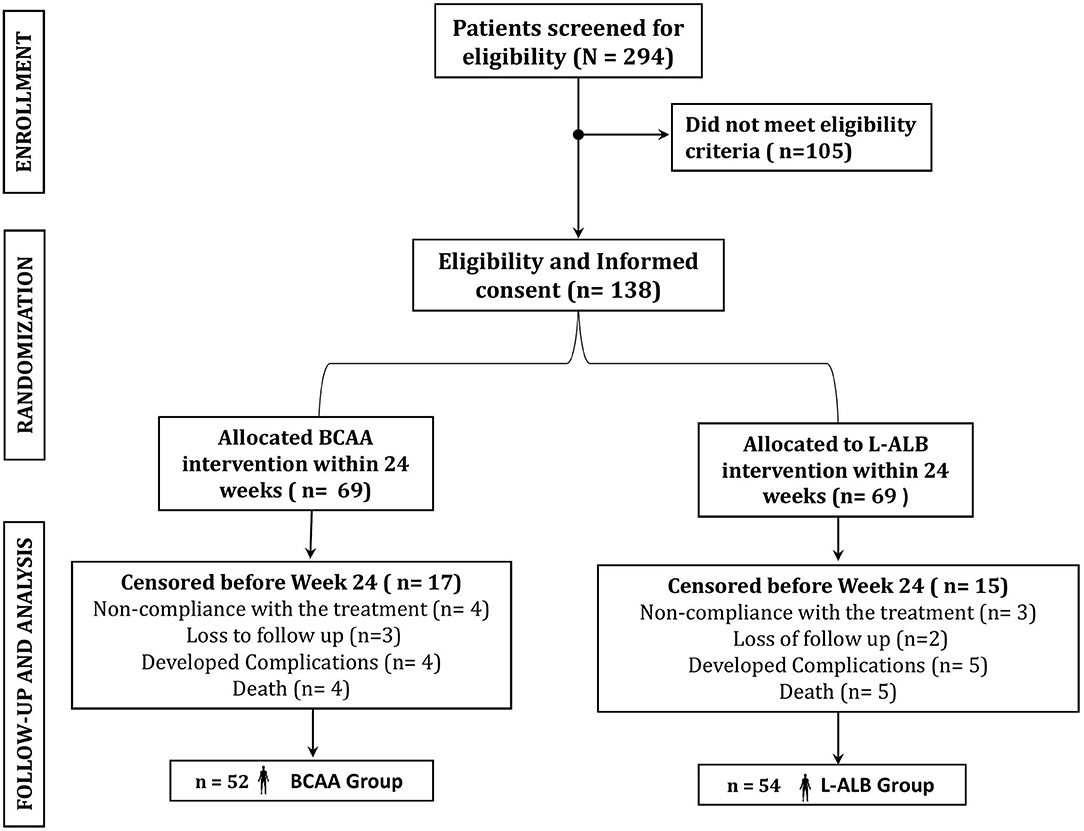
Frontiers | Impact of Branched Chain Amino Acid on Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength, Physical Performance, Combined Survival, and Maintenance of Liver Function Changes in Laboratory and Prognostic Markers on Sarcopenic Patients With

Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Oral Branched-Chain Amino Acids Supplementation in Athletes: A Systematic Review
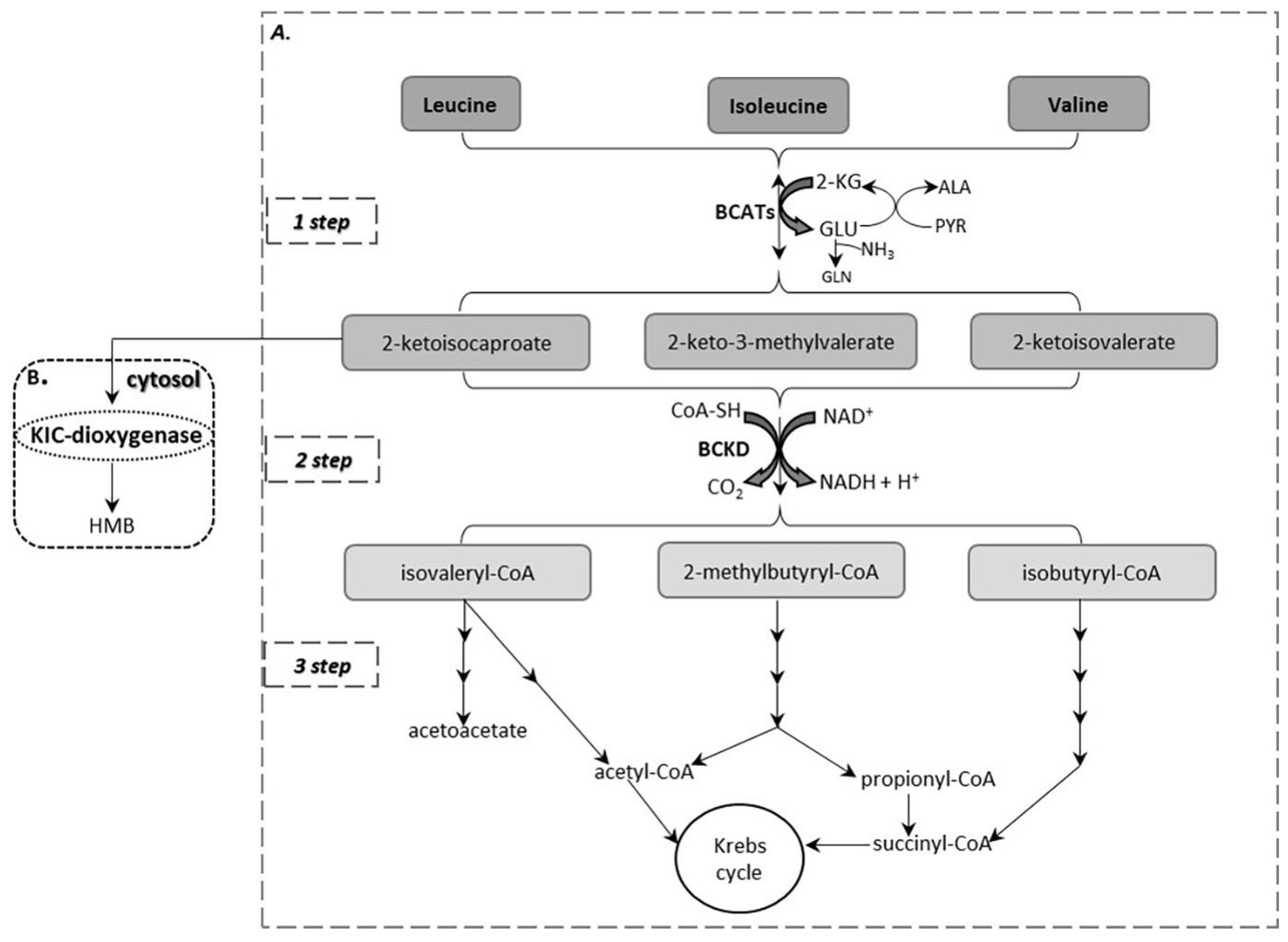
IJMS | Free Full-Text | The Critical Role of the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Catabolism-Regulating Enzymes, Branched-Chain Aminotransferase (BCAT) and Branched-Chain α-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase (BCKD), in Human Pathophysiology
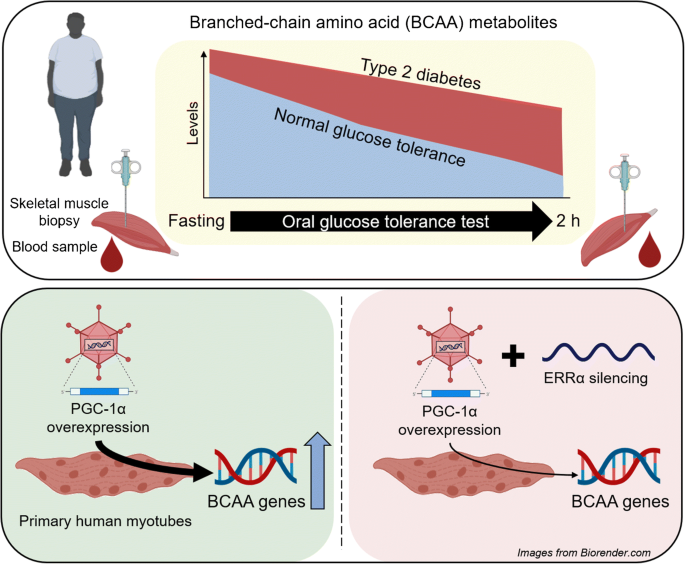
Branched-chain amino acid metabolism is regulated by ERRα in primary human myotubes and is further impaired by glucose loading in type 2 diabetes | SpringerLink

Muscle-specific deletion of BDK amplifies loss of myofibrillar protein during protein undernutrition | Scientific Reports

Lifelong restriction of dietary branched-chain amino acids has sex-specific benefits for frailty and life span in mice | Nature Aging

Branched-chain amino acids and Alzheimer's disease: a Mendelian randomization analysis | Scientific Reports

Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Associations Between Dietary Protein Sources, Plasma BCAA and Short-Chain Acylcarnitine Levels in Adults
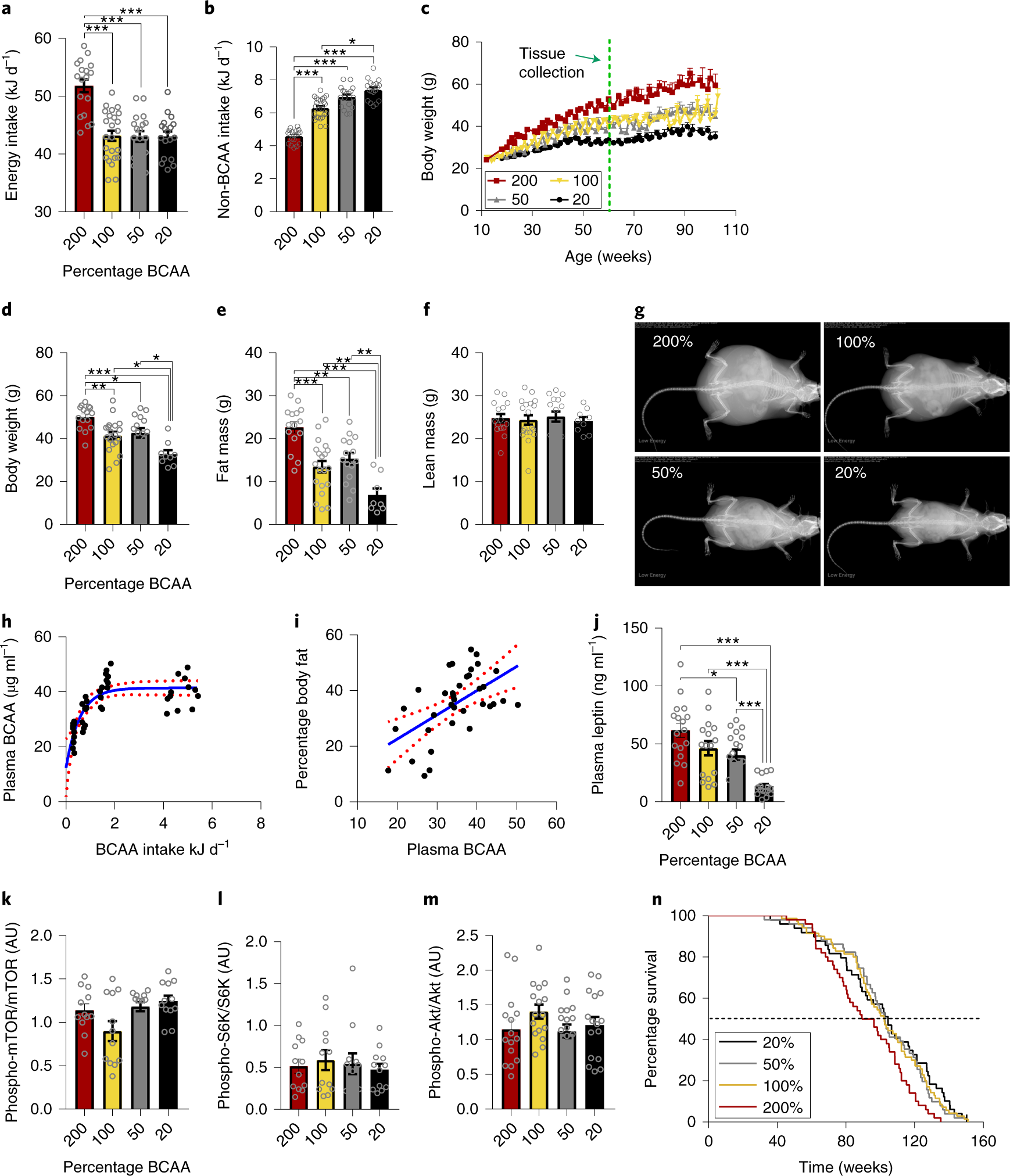
Branched-chain amino acids impact health and lifespan indirectly via amino acid balance and appetite control | Nature Metabolism
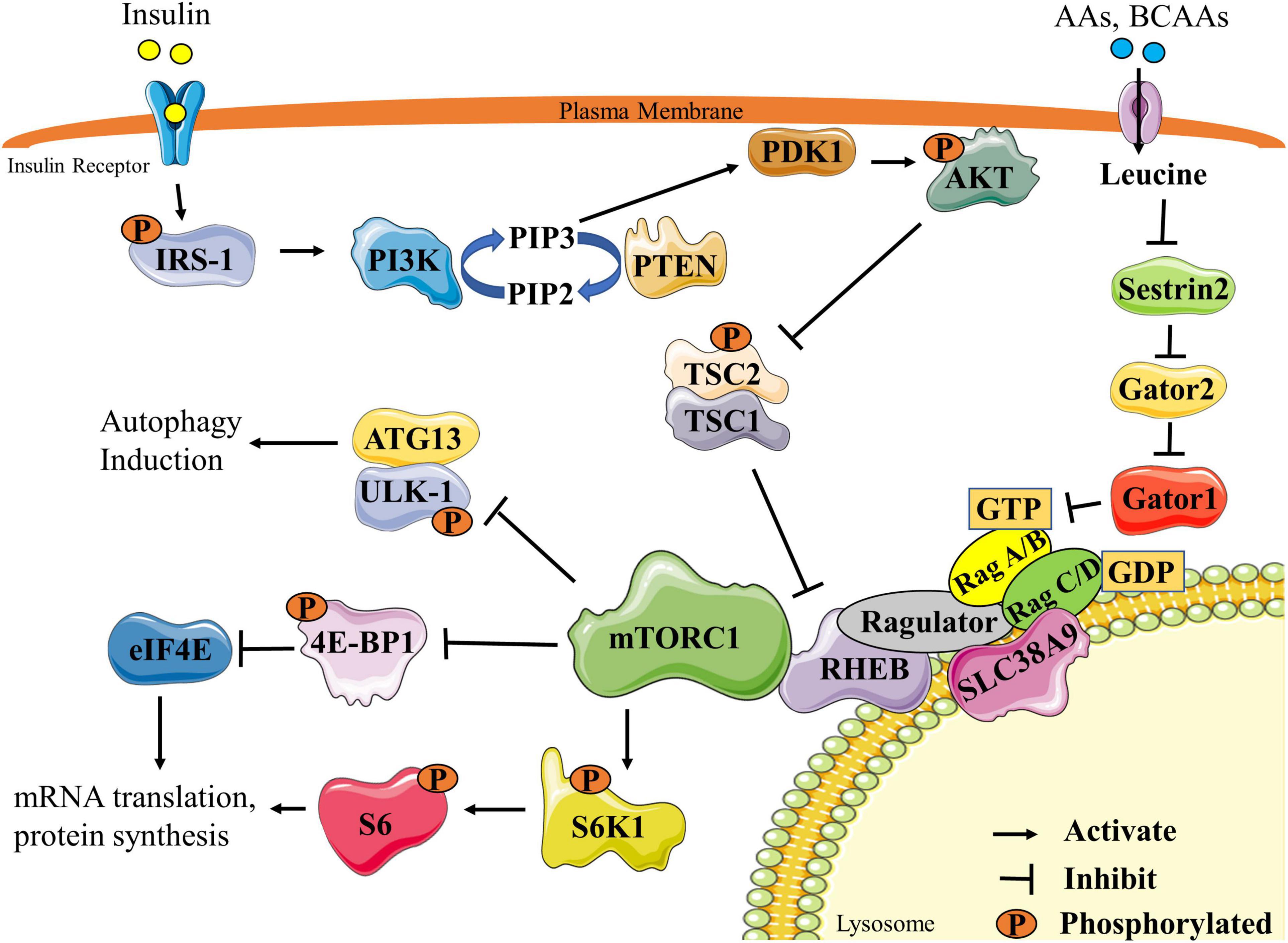
Frontiers | Branched-chain Amino Acids: Catabolism in Skeletal Muscle and Implications for Muscle and Whole-body Metabolism