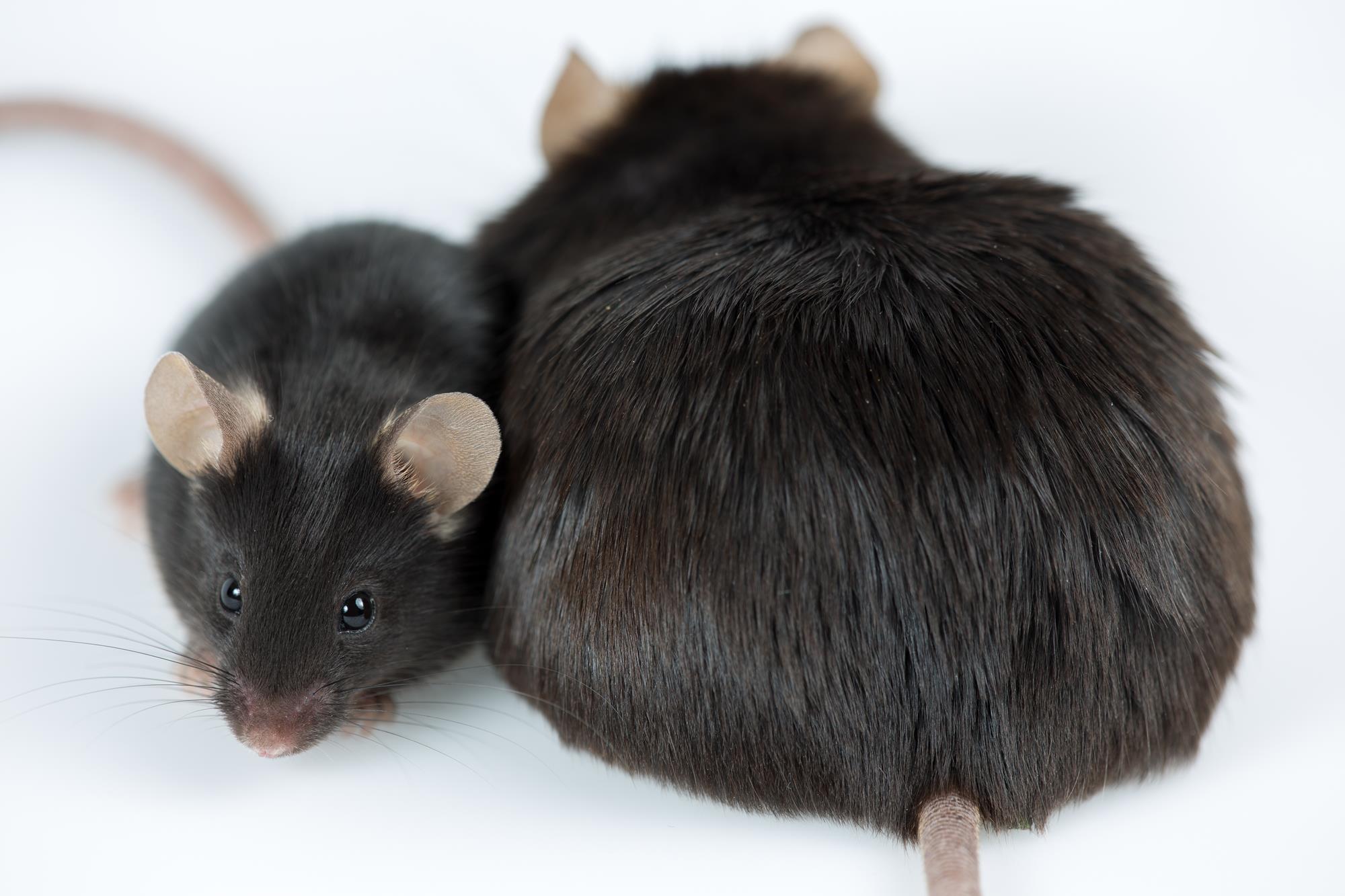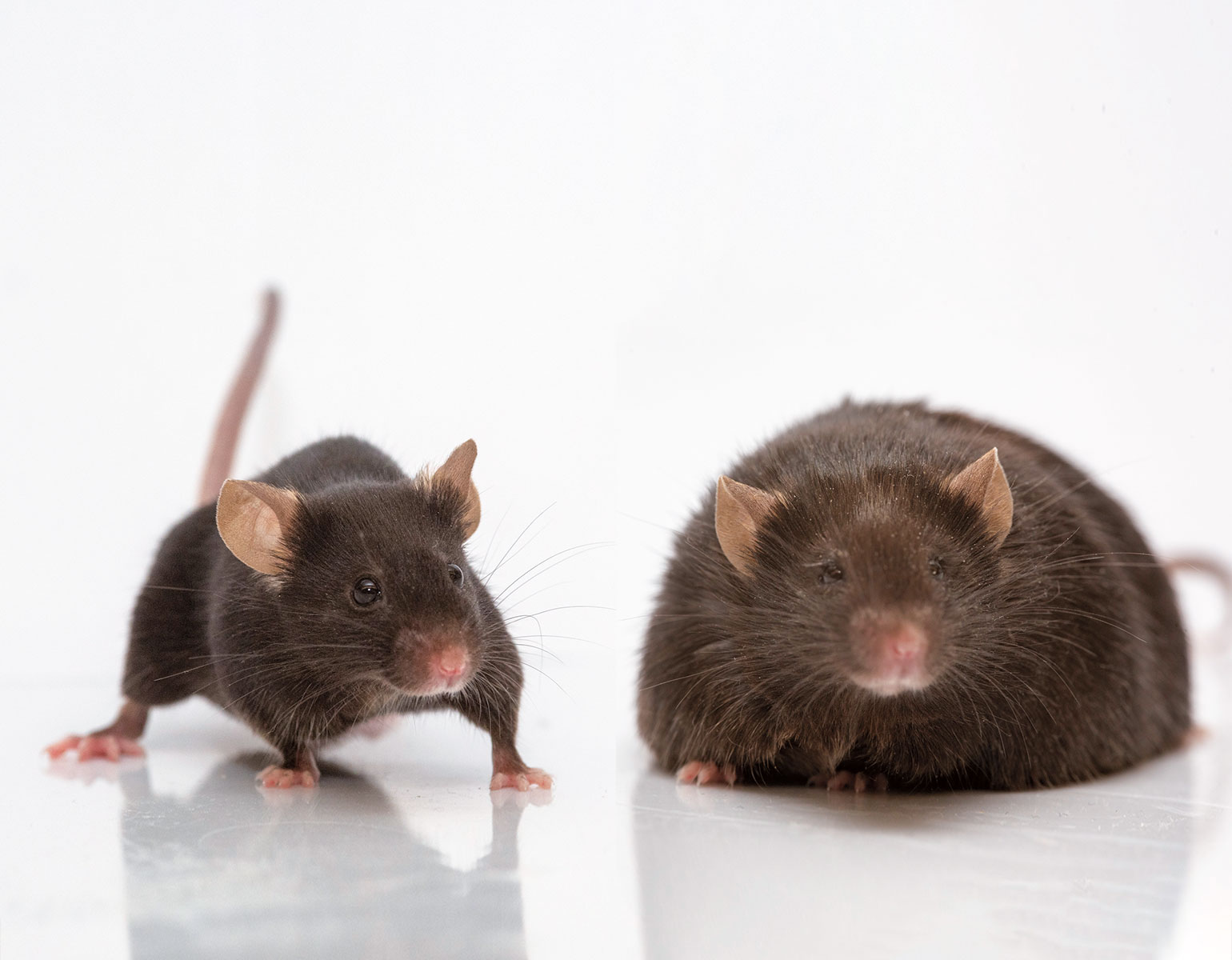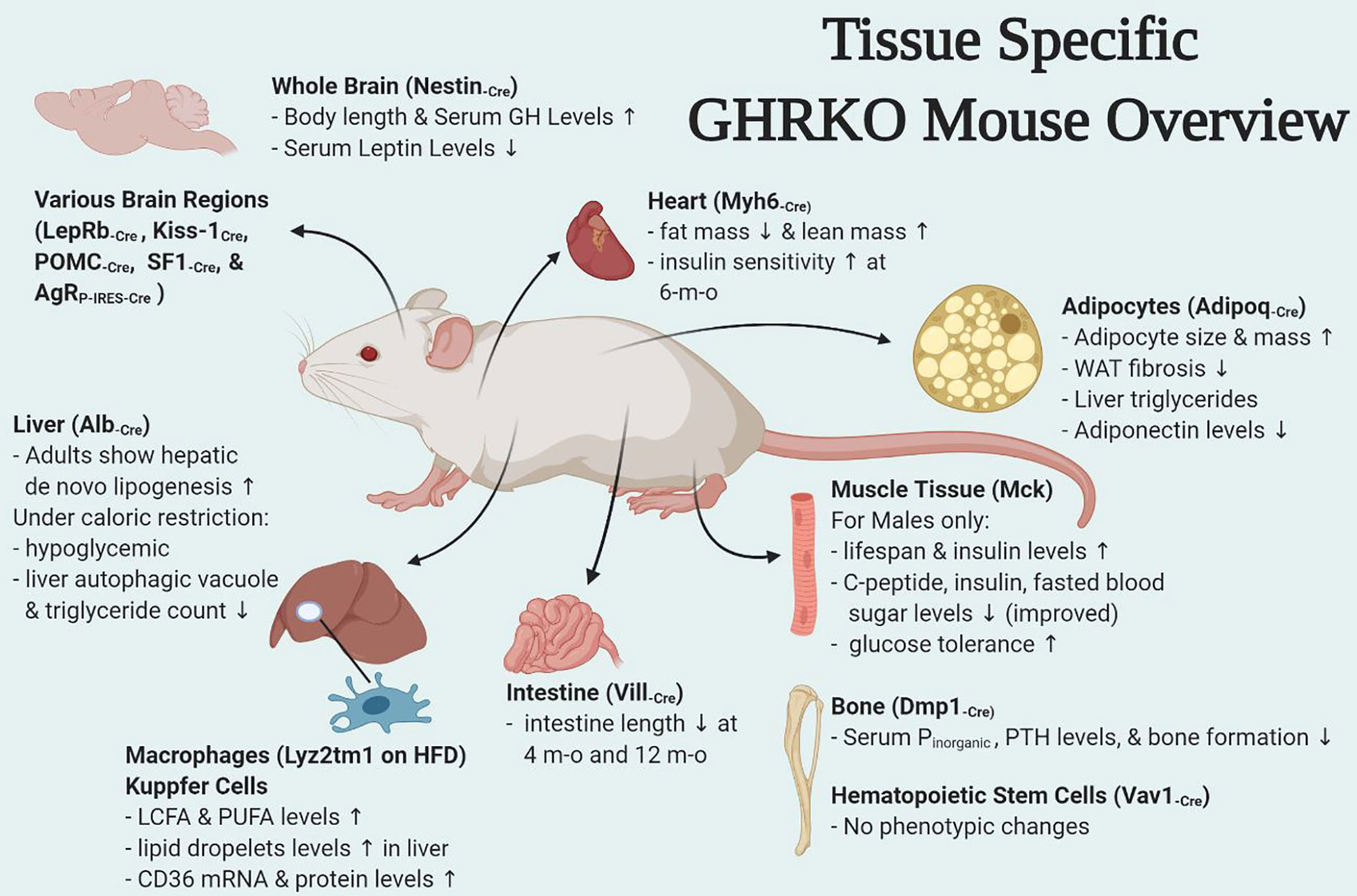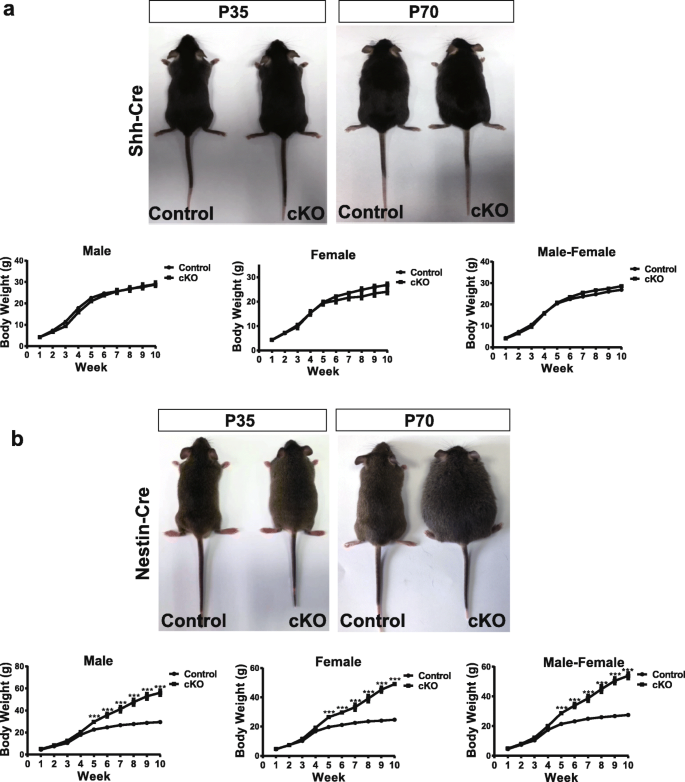
Conditional knockout of leptin receptor in neural stem cells leads to obesity in mice and affects neuronal differentiation in the hypothalamus early after birth | Molecular Brain | Full Text

Loss of Sex-Specific Difference in Femoral Bone Parameters in Male Leptin Knockout Mice | SpringerLink

K5-leptin skin graft-mediated correction of obesity in immunodeficient... | Download Scientific Diagram
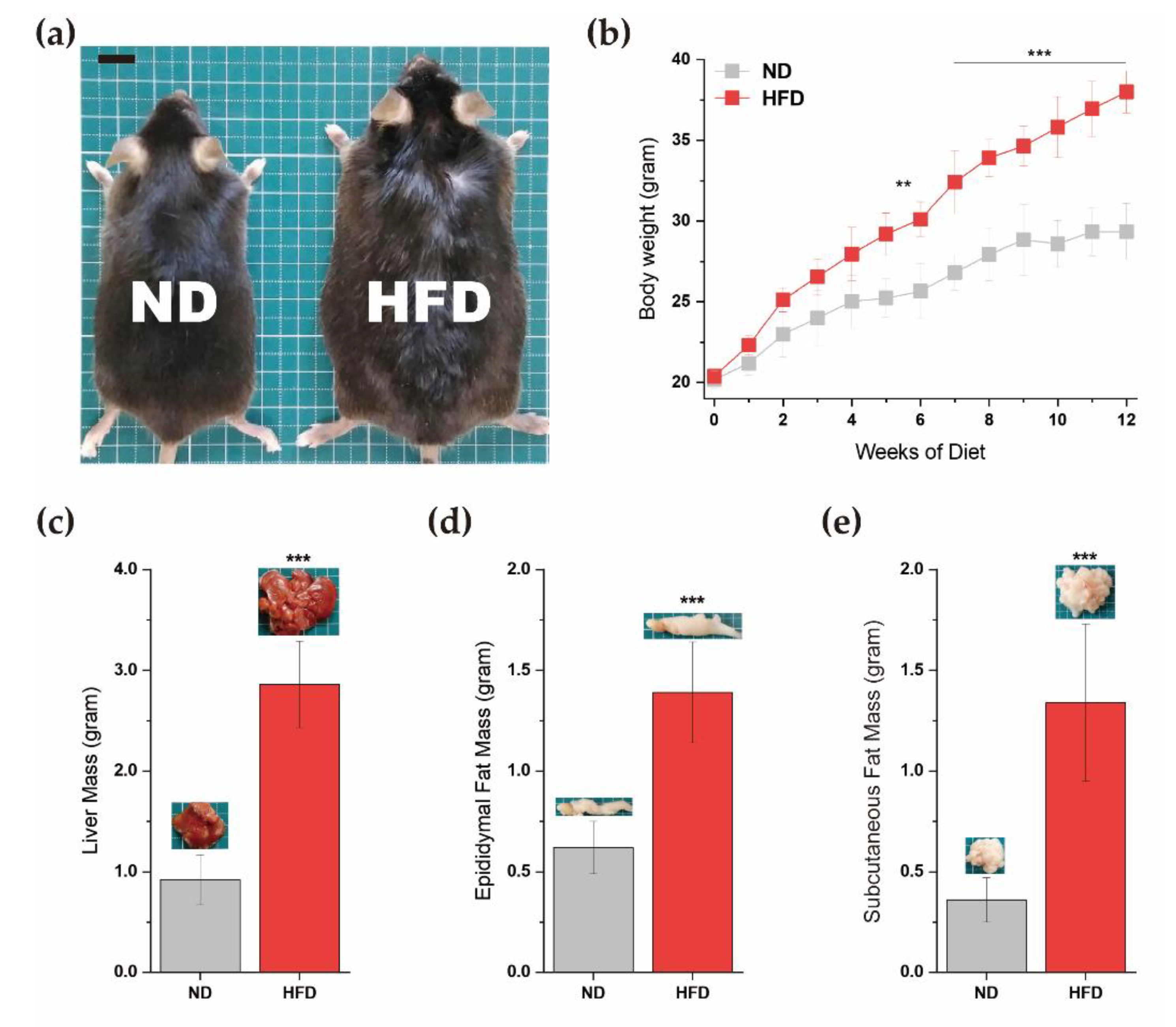
Biosensors | Free Full-Text | Sandwich ELISA-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Leptin in Control and Diet-Induced Obesity Mouse Model

Gender differences between hypocretin/orexin knockout and wild type mice: age, body weight, body composition, metabolic markers, leptin and insulin resistance - Ramanathan - 2014 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library

Leptin deficient ob/ob mice and diet-induced obese mice responded differently to Roux-en-Y bypass surgery | International Journal of Obesity

Physical appearance of mice following rAAV-leptin treatment. Mice were... | Download Scientific Diagram

Leptin Rapidly Improves Glucose Homeostasis in Obese Mice by Increasing Hypothalamic Insulin Sensitivity | Journal of Neuroscience